Managing diabetes requires meticulous care, especially when it comes to storing insulin. Insulin is a crucial medication for many diabetics, and it must be stored properly to maintain its efficacy. This can become particularly challenging while traveling. This article delves into various strategies to keep insulin cold while on the move, ensuring it remains effective for those who depend on it.
How to Store Insulin When Traveling
The primary concern with insulin storage is maintaining the right temperature. Insulin must be stored between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F) until its first use. Once opened, it can generally be kept at room temperature, below 30°C (86°F), for up to 28 days. However, exposure to extreme temperatures can degrade its potency.
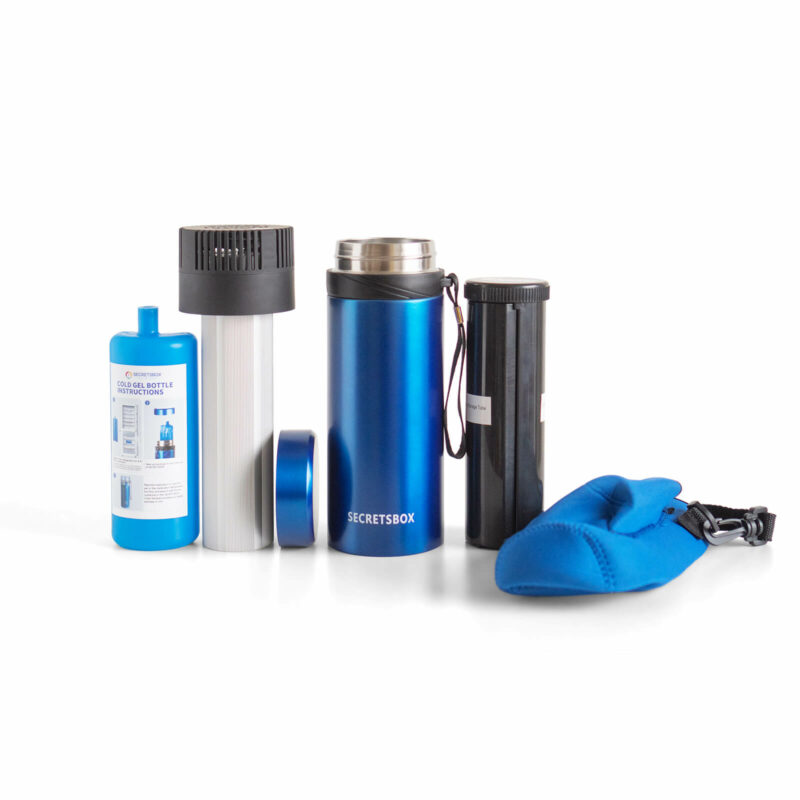
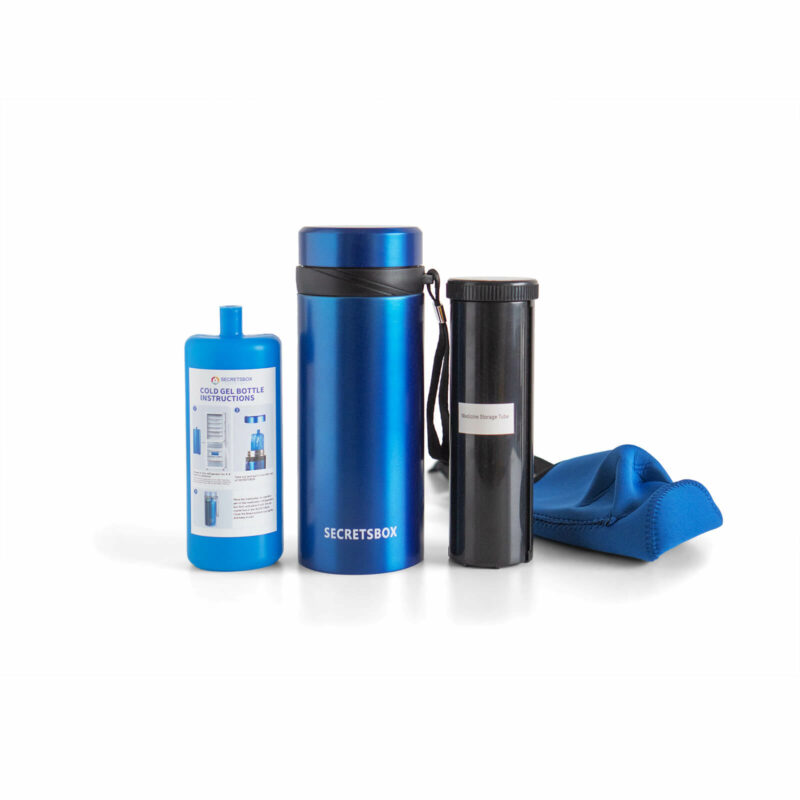
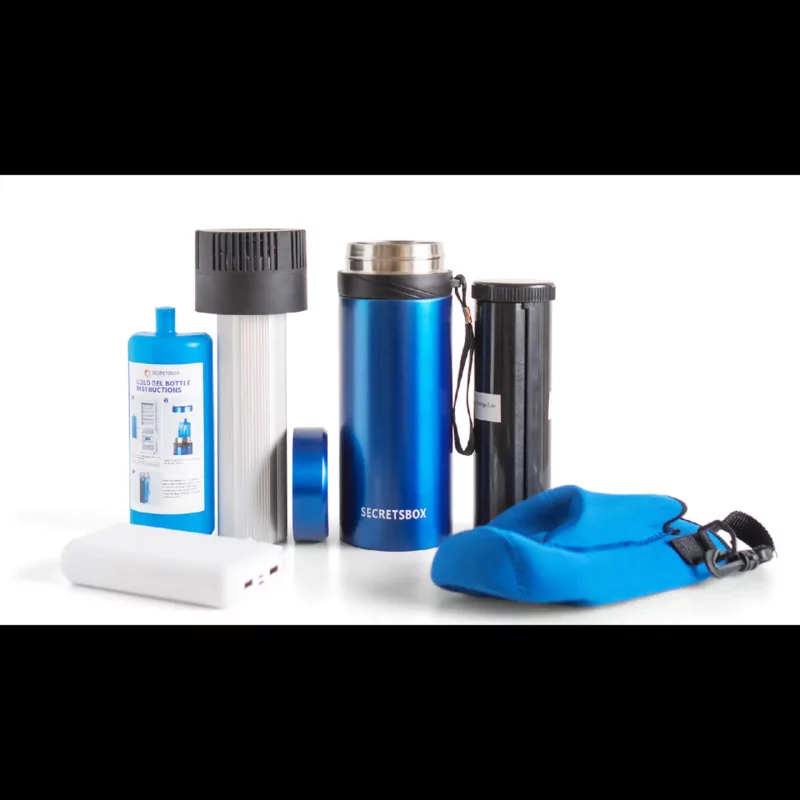
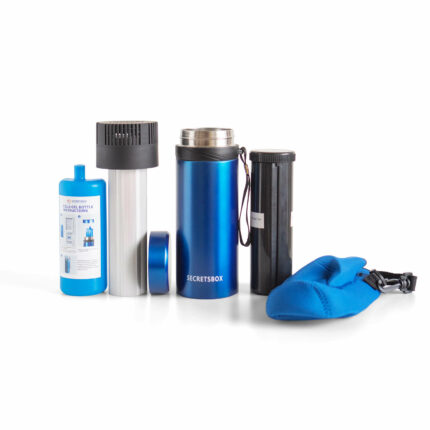
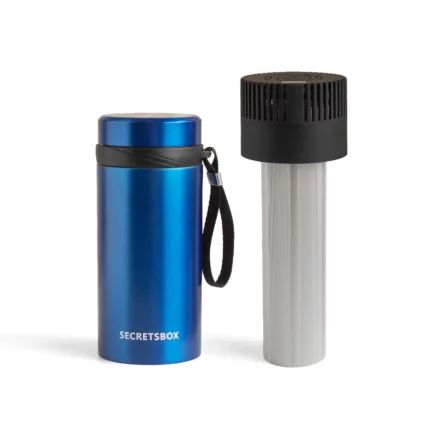
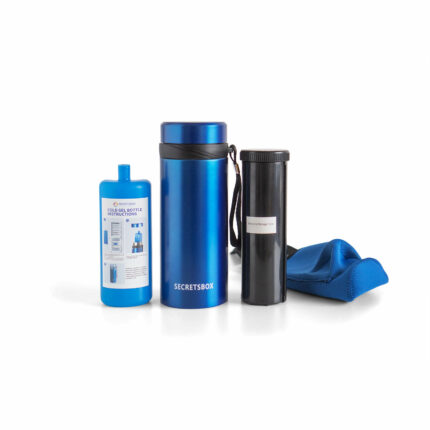
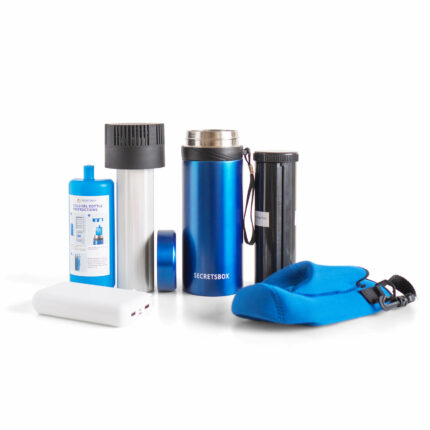
Using Insulated Cooling Cases
Insulated cooling cases are specifically designed for storing insulin. They have cooling gel packs or panels that can be pre-chilled and inserted into the case to keep insulin at the correct temperature for several hours. It’s crucial to avoid direct contact between the insulin and ice packs to prevent freezing.
Portable Medical Refrigerators
For longer trips, a portable medical refrigerator can be invaluable. These devices are designed to maintain a steady temperature and can be powered through various means, including AC outlets, car adapters, and even battery packs.
Where to Store Insulin While On the Move
Choosing the right place to store insulin while traveling is as important as how you store it.
In Carry-On Luggage
When flying, always keep insulin in your carry-on luggage. Checked luggage can be subjected to extreme temperatures and rough handling. The cabin’s controlled environment is safer for temperature-sensitive medications.
Avoiding Direct Sunlight and Heat Sources
Always store insulin away from direct sunlight and heat sources. In a car, for example, don’t leave insulin in the glove compartment or on the dashboard. Instead, keep it in a cooler bag in the main cabin.
Why It’s Important to Keep Insulin Cold
Keeping insulin at the correct temperature is not about prolonging its shelf life alone; it’s about preserving its potency. Insulin exposed to temperatures outside the recommended range can become less effective, which can lead to poorly controlled blood sugar levels and pose serious health risks.
Tips for Traveling with Insulin
- Monitor Insulin Regularly: Regularly check the insulin’s appearance. If it looks cloudy or has particles (and it’s not a type of insulin that is supposed to look that way), it might have been compromised.
- Pack Extra Supplies: Always pack more insulin than you think you’ll need, along with extra cooling packs or devices. Delays and unexpected events can extend your trip.
- Prepare for Time Zone Changes: Traveling across time zones can affect your dosing schedule. Consult with your healthcare provider on how to adjust your insulin regimen accordingly.
Traveling with insulin requires careful planning and the right tools. By understanding how to store insulin correctly and where to keep it while on the move, you can manage your diabetes effectively, even when away from home. Always consult with a healthcare provider before traveling to ensure your plan for storing insulin aligns with your medical needs.
References
This article is based on general guidelines for insulin storage and diabetes management. For specific advice and information, please consult with healthcare professionals or refer to the following authoritative sources:
- American Diabetes Association (ADA)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) on Traveling with Diabetes
- Insulin Storage and Switching Between Products in an Emergency by the FDA
Remember, managing diabetes effectively while traveling is entirely possible with the right preparation and knowledge.